Editor’s note: Robert Wiltbank, PhD, is a professor at Willamette University, where he and Wade Brooks run an angel investing fund managed by second-year MBA students. He is on the board of the Angel Resource Institute, and is a partner with Montlake Capital (a late stage growth capital fund) and with Revenue Capital Management (a royalty based lender). He’s c0-authored two books and many academic articles.
I began studying angel investing returns about 10 years ago as a result of a problem I couldn’t resolve: The investing world seemed certain that angel investors were rubes. Conventional wisdom dictated that they made reckless investments in very early-stage ventures mostly doomed to fail. And whenever they might come close to succeeding, savvy “professional” investors would just swoop in, cram them down, and win the real returns. In addition, angels were up against a selection problem: All the best entrepreneurs and opportunities would naturally gravitate to the best venture capital funds, leaving only the “scraps” for angel investors.
So which is it? Are angel investors just unwitting philanthropists or legitimate entrepreneurial investors?
Through research backed by the Kauffman Foundation, NESTA (a UK-based entrepreneurship foundation), the University of Washington, and Willamette University, I’ve compiled the largest data set on angel investor financial returns that exists. The angel investors I was spending time with didn’t seem so naïve or incompetent. While not professional investors, most angels are very successful in their own right, overwhelmingly as a result of their own entrepreneurial endeavors. Their firsthand knowledge of creating new businesses and new markets seemed quite relevant to successfully investing in other entrepreneurs working to do the same.
The best estimate of overall angel investor returns from this data is 2.5 times their investment, though in any one investment the odds of a positive return are less than 50 percent. This is absolutely competitive with venture capital returns.
The interest in Andy Rachleff’s article suggesting that angel investors don’t make money has been extensive. The piece is thought-provoking and makes several really good points. First, everyone should understand that angel investing is high-risk investing; it really is a “homerun” game like formal venture capital investing. Second, a portfolio of investments, even in angel investing, is a great approach. Third, whenever you’re making risky investments it is a great principle to limit your bet size and make sure that you don’t put too much of your wealth into aggressive positions. Valuable lessons learned from Andy’s personal experience venture investing in Silicon Valley.
Fortunately there is now good data on angel returns in Silicon Valley and nationally, and while more research is certainly needed, the data suggest that angel investors can and often do make money. Of course there are more and less capable angel investors, just as with formal VCs, but as a group they are definitely not unwitting philanthropists. They appear to generate credible returns as entrepreneurial investors.
With this data, we don’t need to make deductions from the experience of venture capitalists. Andy says: “If the average VC fund barely makes money, and seed investments represent even less compelling opportunities than the ones pursued by venture capital firms, then the typical return for angels must be atrocious.” Only they’re not. Deductions like this are problematic because early-stage venture investing does not happen in an efficient market. Angel investors often act differently than VCs, and the fact that VCs abandoned seed-stage investing doesn’t necessarily mean they did so because seed investments are inherently less compelling. (A plausible alternative explanation of why VCs backed out of seed stage investing is as a consequence of a growth in fund size, NOT a reduction in the number of compelling opportunities at the seed stages.)
Let’s take a look at the actual data. (If you are big into data, you can read two reports detailing the data collection efforts in both the U.S. and the U.K., as well as a more detailed description of the distribution of outcomes: Kauffman Foundation Angel Returns Study and NESTA Angel Investing Study. In addition to those two practitioner reports, you can read a more formal academic paper on how entrepreneurial expertise influences the returns experienced by angel investors.]
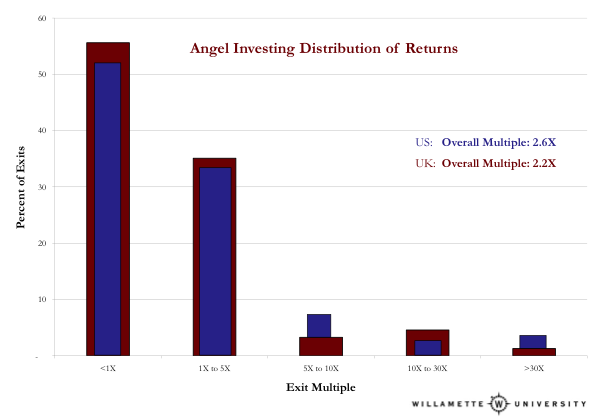
The overall multiple from the data represented in the graph is 2.5 times the angel investment (i.e. $100,000 invested, would return $250,000). It is based on more than 1,200 exited investments made by angel investors over a 15-year timeframe, collected separately across both North America and England. It is not highly concentrated geographically, or in the bubble of 1998-2000, or in any industry. The distribution of returns from the different U.S. and UK samples is virtually identical — a useful robustness check on the initial North American data. There are no “carried value” estimates in the data. (If you want more detail on these things, you can go crazy in the full reports.)
Here are some important things to note:
- In any ONE investment, an angel investor is more likely than not to lose their money, i.e. to earn less than a 1X return. It is risky. However, once investors had a portfolio of at least six investments, their median return exceeded 1X. Irving Ebert, of the Ottawa Angels, has done some outstanding Monte Carlo simulation with this data, finding that making near 50 investments approximates the overall return at the 95th percentile. Most investors will be somewhere in the middle, of course. Angel investors probably should look to make at least a dozen investments, but that’s just a rule of thumb. This is critical: Each investment has to be done as though it’s your only one; the bar can’t be lowered to enable you to more quickly build a bad portfolio.
- The production of cash is highly concentrated in winners; 90 percent of all the cash returns are produced by 10 percent of the exits. This is essentially the same concentration as in venture capital. The next largest “bucket” of cash returns is in the high-volume, but low-multiple group, the 1X to 5X category. It’s important to note, however, that it’s not exactly the same as formal venture capital. These returns happened all over the place geographically (NOT all in the Bay Area or Boston), happened across industries, and most often happened without having any follow-on investment from VCs. In fact, VCs eventually invested in only one out of three of the ventures, and the ventures in which they did invest produced lower returns than those where VCs did not invest.
- When you aggregate all of the data, these angel investors (across the U.S. and UK) produced a gross multiple of 2.5X their investment, in a mean time of about four years. This return is absolutely competitive with formal venture capital returns. Because the margin of error around these estimates is larger than that from the venture source and venture expert data, I won’t assert that angels “outperform” formal VCs. But to assume that they are fooling themselves about making money in angel investing is simply unsupported by the data.
Angel investors seem to bring more variety to the strategies in how they invest and build companies, relative to formal venture capital. Their entrepreneurial experience (85 percent of them are “cashed out” entrepreneurs), and the fact that they are investing their own money, makes the idea that they are just “hack” VCs a little off base. They are different than formal VCs. Some investors focus on capital efficiency, some on shooting the moon with as much capital as they can get. Some actively seek VC involvement, some deliberately avoid VC involvement. Many other approaches develop all of the time.
But before we get too far away from hard data, over the last year or two the Angel Resource Institute (ARI) has been building the HALO Report, a quarterly report on group angel investor activity in the U.S. The data on valuations, activity levels, geographic and industry distribution is quite interesting, and over time, this will provide a quarterly gauge on angel investment returns, as well. For the first half of this year, valuations aren’t outlandish, at about $2.7 million pre-money, and round sizes are right around $550K, spread throughout a variety of industries. The picture again seems more representative of angels as legitimate entrepreneurial investors. It’s also worth noting that angel investing is spread more widely throughout the country than formal venture capital; it’s not highly concentrated in the Bay Area.
To keep things in perspective, it’s important to remember that most ventures, even great ones, don’t ever take venture capital investment. A little less than one-third of IPOs are of venture capital-backed firms. While this is really impressive given that VCs invest in less than 1 percent of new ventures, it still means that two out of every three IPOs are of companies that never had any venture capital investors. Angel investors, like savvy entrepreneurs, don’t necessarily view raising formal venture capital investment as a measure of success.
No one celebrates taking out a loan, but for some reason some people like to celebrate taking on venture investment. Best case: equity investment (whether angel or VC) is a tremendous asset with a commensurate financial obligation. Worst case: it’s an albatross around your neck…with a commensurate financial obligation.
Just like angel investors, VCs want their money back — times 50 if they can get it. The idea that angels are suckers while VCs have cornered the market on building great companies is simply not supported by the data. Now let’s get back to the business of selling more product and less stock!































Comment